ADAPTER
Convert the interface of a class into another interface which clients expect. (AKA Wrapper)
Scenario
- You want to use existing class but its interface doesn’t match the one you need.
- create reusable class that cooperates with unrelated or unknown classes
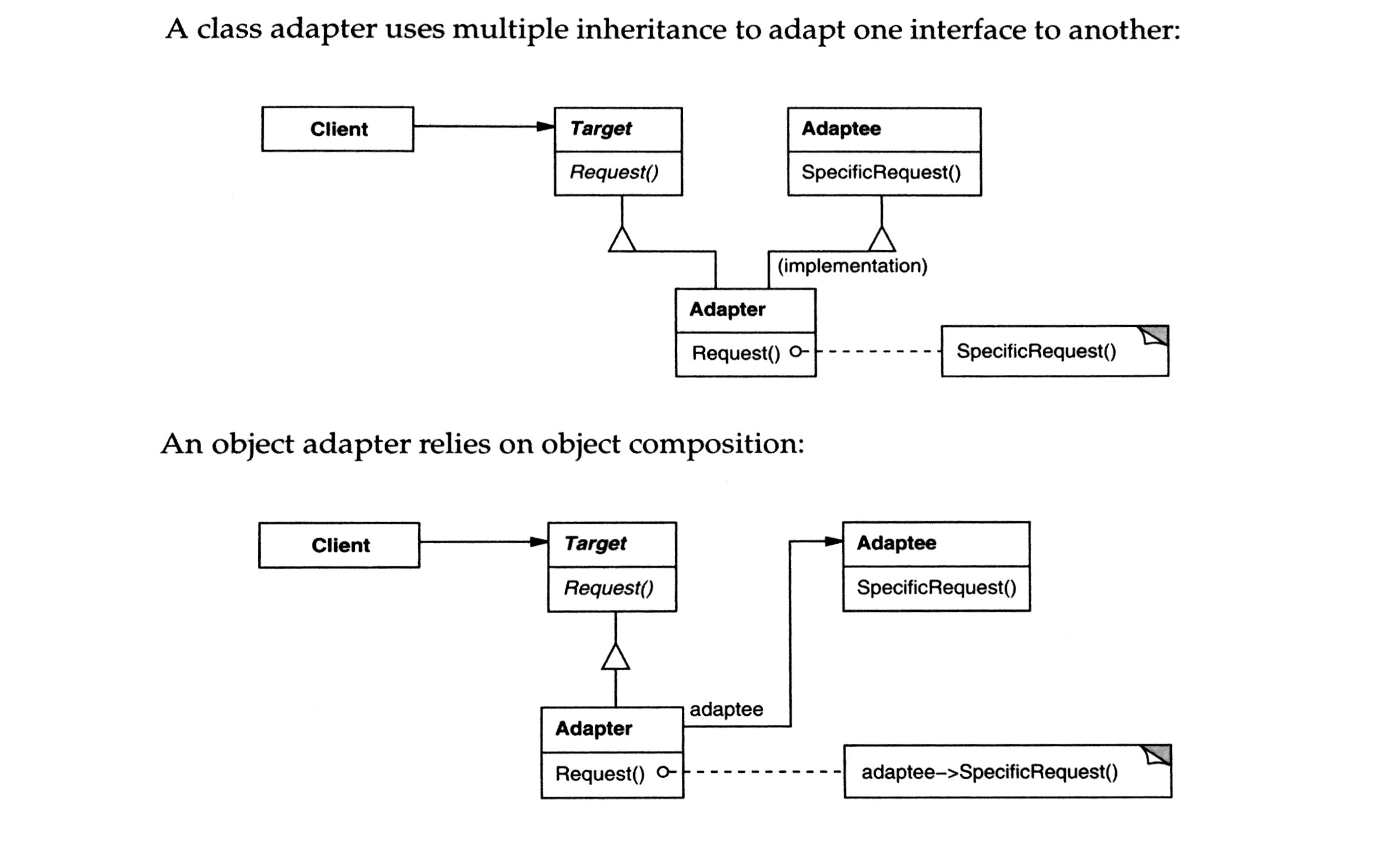
Participants
- Target
- defines the interface that Client wants.
- Adaptee
- define existing interface that needs adapting
- Adapter
- adapts the interface of Adaptee to the Target
Example
class Dog(object):
def __init__(self):
self.name = "Dog"
def bark(self):
return "woof!"
class Cat(object):
def __init__(self):
self.name = "Cat"
def meow(self):
return "meow!"
class Adapter(object):
"""
Adapts an object by replacing methods.
Usage:
dog = Dog
dog = Adapter(dog, dict(make_noise=dog.bark))
>>> objects = []
>>> dog = Dog()
>>> print(dog.__dict__)
{'name': 'Dog'}
>>> objects.append(Adapter(dog, make_noise=dog.bark))
>>> print(objects[0].original_dict())
{'name': 'Dog'}
>>> cat = Cat()
>>> objects.append(Adapter(cat, make_noise=cat.meow))
>>> human = Human()
>>> objects.append(Adapter(human, make_noise=human.speak))
>>> car = Car()
>>> car_noise = lambda: car.make_noise(3)
>>> objects.append(Adapter(car, make_noise=car_noise))
>>> for obj in objects:
... print('A {} goes {}'.format(obj.name, obj.make_noise()))
A Dog goes woof!
A Cat goes meow!
A Human goes 'hello'
A Car goes vroom!!!
"""
def __init__(self, obj, **adapted_methods):
"""We set the adapted methods in the object's dict"""
self.obj = obj
self.__dict__.update(adapted_methods)
def __getattr__(self, attr):
"""All non-adapted calls are passed to the object"""
return getattr(self.obj, attr)
def original_dict(self):
"""Print original object dict"""
return self.obj.__dict__
BRIDGE
Decouple an abstraction from its implementation.
Scenario
- Avoid permanent binding between an abstraction and its implementation. Allow easy implementation switch in the future
- Both implementation and abstraction needs to be extensible by subclassing. Allow different combination of abstraction and implememation
- share implementation among multiple objects
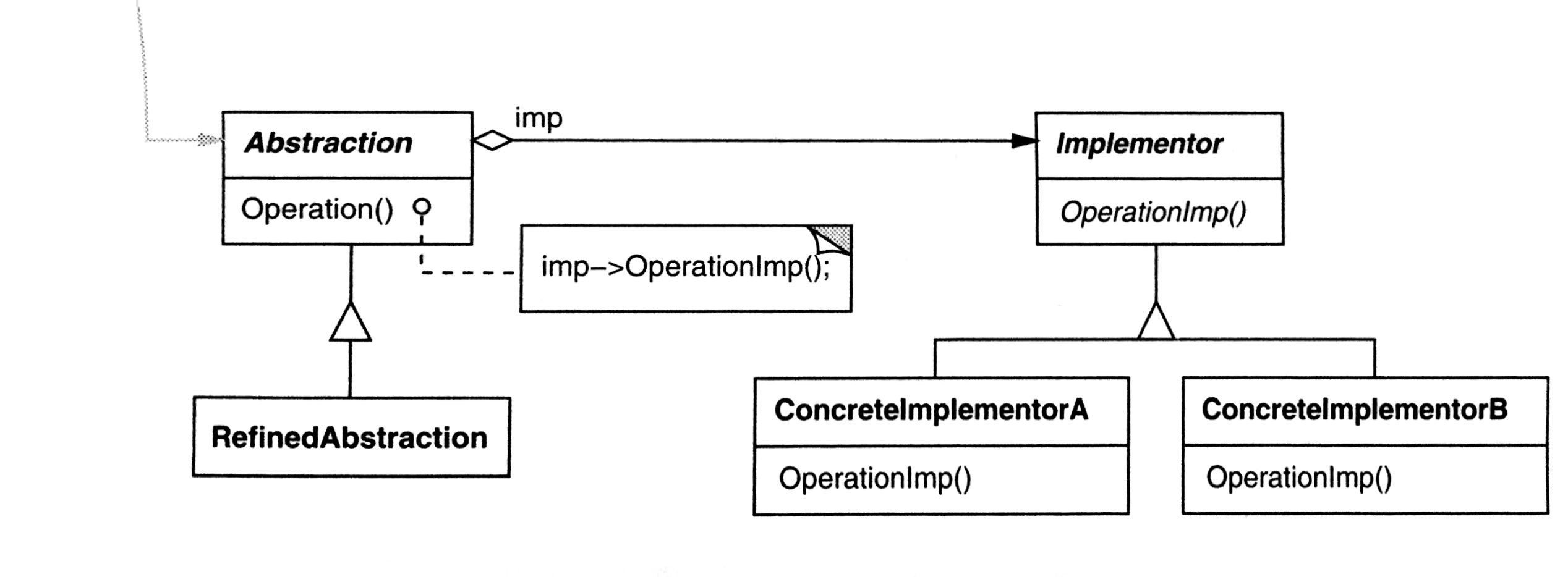
Participants
- Abstraction
- define model interface
- maintains a reference to an object type implemetor
- RefinedAbstraction
- Extends the interface defined by Abstraction
- Implementor
- define the implementation classes. The interface can be different from the abstraction and focus on primitive operations.
- ConcreteImplementor
- implements the implementor interface
- Usually combine with AbstractFactory to get the correct Implementor
Example
class Window {
...
WindowImp* window::GetWindowImp() {
if (_imp == 0)
_imp = WindowSystemFactory::Instance()->MakeWindowImp();
}
return _imp;
private:
WindowImp* _imp; // refrence to window implemation
}
class WindowImp {
...
}
COMPOSITE
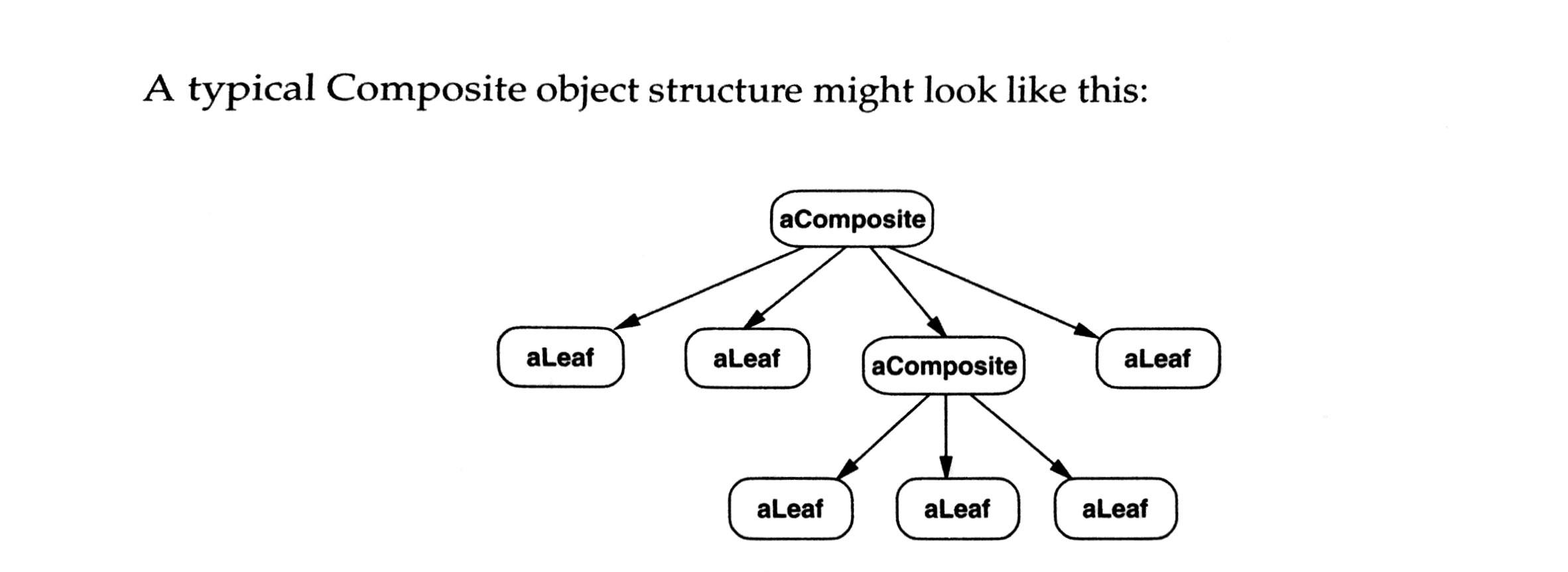
Compose objects into tree structures to represent hierarchies. Give same representation to individual objects and compositions of objects.
Scenario
- represent part-whole hierarchies of objects
- client can ignore the difference between compositions of objects and individual objects.
- i.e., draw a picture. which has different types and group of types. To draw the whole image, just call graph.draw(). it should go through all objects and group of objects inside to draw everything.
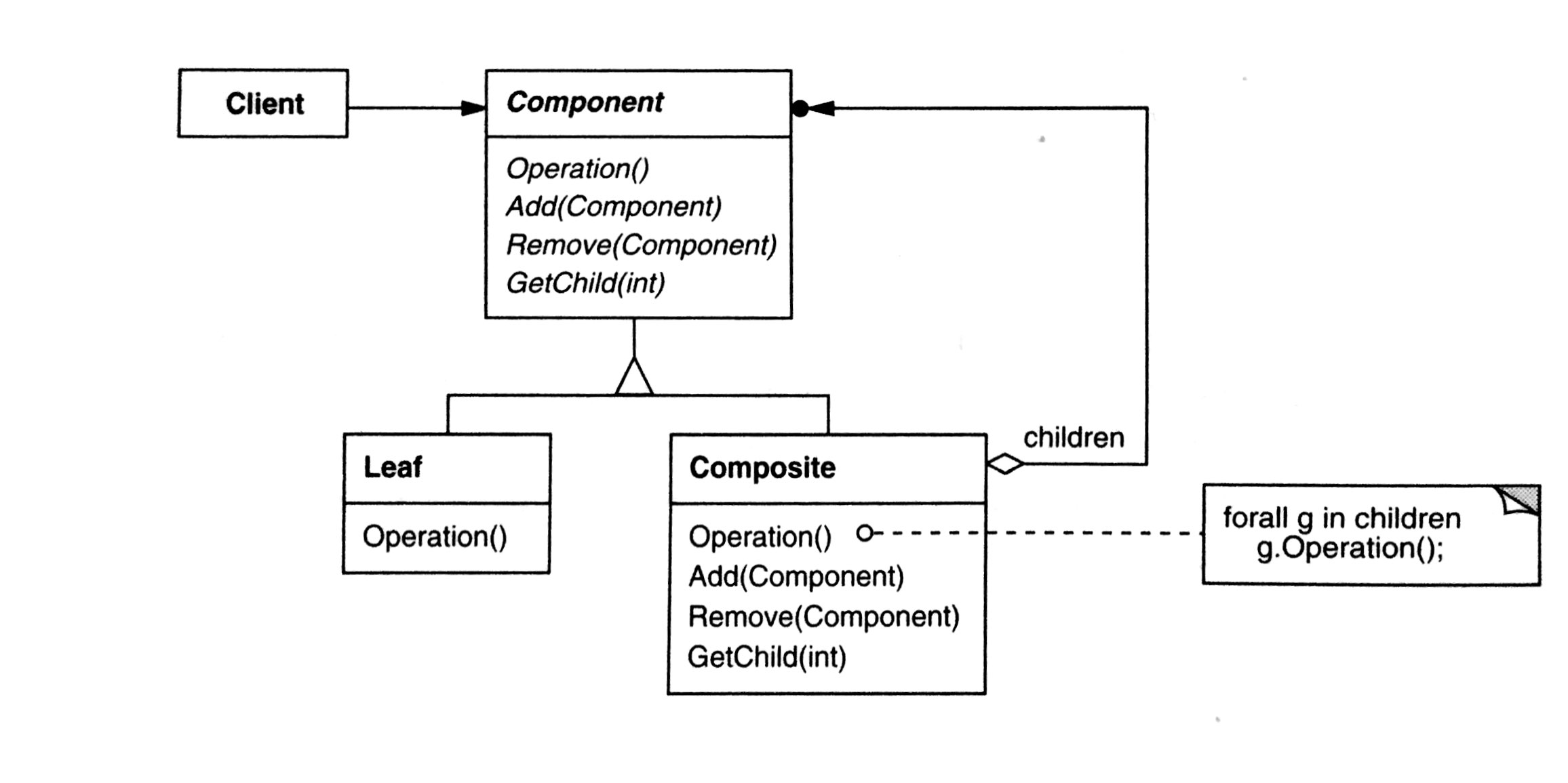
Participants
- Component
- base class for both object and compositions
- define common interfaces
- declares an interface to accessing and managing its child components
- (optional) can have a pointer to parent
- Leaf
- individual objects, no children
- for method of accessing/managing child, just throw error
- Composite
- store child components
- implements child-related operations
Example
class Equipement {
public:
virtual int NetPrice(); // common operation
virtual void Add(Equipment*); // add child
virtual void Remove(Equipment*); // remove child
}
class CompositeEquipment: Public Equipment {
// impement real child access methods.
private:
List<Equipment*> _equipment;
// for NetPrice: return sum(child in _equipment)
}
Cabinet* cabinet = new Cabinet();
Chassis* chassis = new Chassis();
cabinet->Add(chassis);
Bus* bus = new Bus();
chassis->Add(bus);
cout << cabinet->NetPrice() <<endl;
